- GF/ SF - Tejas, Opp Hotel Prasadalay, Shukrawar Peth, Pune - 411002
- +91 90 2132 2132
Quick Commerce: An Industry of Fast, On-Demand Shopping

It was in 2015 when someone felt hungry and was either too lazy to cook or too lazy to dine out at a restaurant. Instead, they placed their order through Zomato. It began with food, and over time, like all evolving technologies, today we see quick commerce catering to groceries, electronics, kitchen items, and other daily needs.
Quick commerce has grown into an industry of its own, with brands like Swiggy, Blinkit, Zepto, and other local players meeting the needs of their communities.
In India alone, the industry is valued at over $3 billion.
In this article, we will explore what quick commerce is, how it differs from e-commerce, and what it takes to succeed in this commerce space.

What is Quick Commerce?
Quick commerce, also called q-commerce, is a type of e-commerce where products are delivered to customers in minutes instead of days. Traditional e-commerce is designed to fulfill a customer’s order within 3-4 days. But in quick commerce, the delivery time can be as less as 10 minutes.
This is achieved through the strategic placement of warehouses, called “dark stores"
Quick commerce operates through mobile apps. Every q-commerce company has its own app that lists products available across different categories. Customers can add items to their cart and pay either online or upon delivery.
So, it is similar to e-commerce. But, what sets it apart is the fast delivery time.
Delivery time is also the key differentiator for these companies in terms of competition.
A major portion of their users comes from urban and semi-urban cities. Most people in these cities have busy schedules, leaving them with little time for grocery shopping, cooking, or other errands. This is the main reason why quick commerce has gained immense popularity among urban and semi-urban populations.
Nowadays, almost every startup enthusiast is considering building a business around quick commerce. But it’s not easy. The task of implementing a quick commerce supply chain comes with a lot of challenges.
To understand this better, we first need to know how it differs from e-commerce.
Differences Between Q-Commerce and E-Commerce
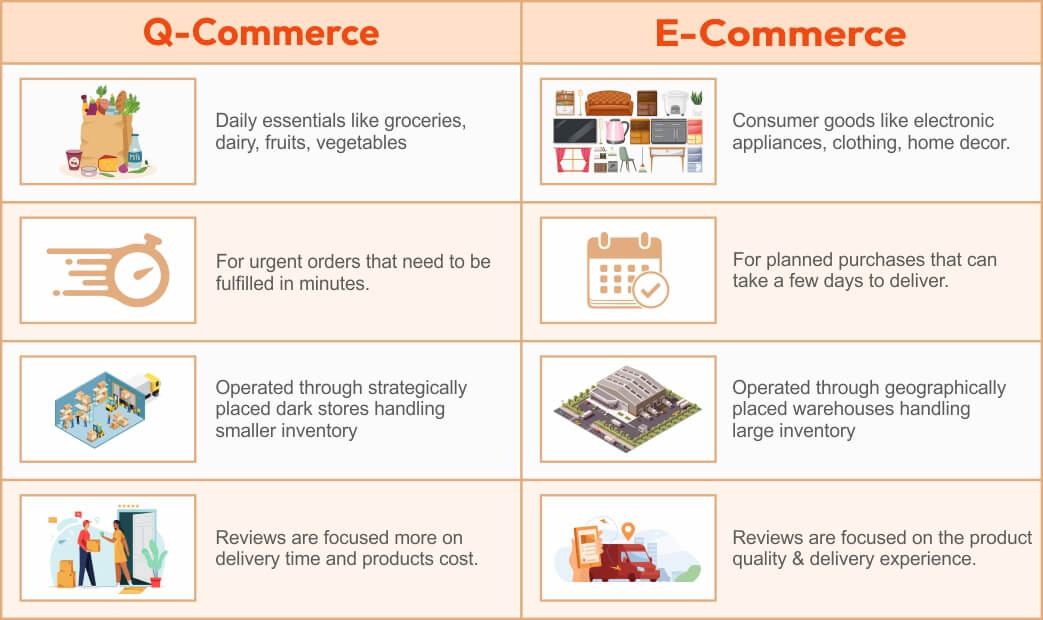
Other than delivery time, as mentioned above, there are a few more aspects that make q-commerce different from e-commerce.
Let’s look at them one by one:
-
Range of Products
The purpose of quick commerce is to fulfill immediate needs. Therefore, the products available on a q-commerce platform are mostly daily essentials like groceries, snacks, dairy, fruits, vegetables, and sometimes kitchen necessities.
On the other hand, e-commerce platforms offer a wide range of products, including electronic appliances, clothing, home decor, and more, providing a comprehensive shopping experience.
-
Delivery Costs
Since quick commerce focuses on fulfilling urgent orders, delivery costs are generally higher. However, e-commerce customers usually make planned purchases and do not expect immediate delivery. They often compare prices across different platforms and wait for seasonal sales to avail maximum discounts.
As a result, delivery times in e-commerce are more flexible, allowing companies to offer free delivery options.
-
Logistics Management
As discussed earlier, q-commerce uses dark stores as fulfillment centers. These dark stores are strategically located based on customer clusters. Setting them up requires thorough data analysis of orders received and identifying regions where potential customers are concentrated.
E-commerce, in contrast, operates through warehouses spread across various geographic regions, with shipments handled in larger quantities.
-
Emphasis on Customer Reviews
Q-commerce places less emphasis on detailed customer reviews and focuses more on delivery time and product quality. The aim is to deliver fresh fruits and vegetables to the customer’s doorstep within 10 minutes. In contrast, e-commerce prioritizes providing a service that encourages customers to leave detailed reviews. Buyers often rely on these reviews before purchasing items like washing machines, coffee makers, or ceiling fans.
Now that we know the differences between the two, let’s explore what it takes to succeed in the q-commerce business. How do these q-commerce giants manage to offer higher discounts and faster deliveries?
Here’s a quick infographic summarizing how quick commerce and ecommerce are different
What aspects decide the success of a quick commerce business?
There are three factors that can make or break any quick commerce business:
- Location of dark stores
- Product listings
- Technology used
Location of Dark Stores
Since delivery time is the key differentiator, the only way to reduce it is by placing dark stores closer to your customers.
While it’s easy to say, finding the perfect location requires extensive data analysis, including insights into customer clusters, order patterns by time of day, availability of delivery executives, and traffic on delivery routes.
Even if data analysis identifies an ideal area for a dark store, challenges may arise, such as no available properties in that location or costs exceeding the company’s budget.
If a business cannot secure its own property, it often seeks help from third-party vendors to lease a dark store.
Inventory Management
Staying updated with product listings is crucial. Stock must be carefully sourced based on trends and the most in-demand items for your customers.
During festive seasons, it’s relatively easy to predict which product categories will see increased demand. However, on non-festive days, regular updates to stock are essential.
A high-end inventory management system is necessary to ensure smooth operations. For example, when a product is sold from a dark store, its barcode is scanned and updated in the system. This allows sourcing vendors to plan the next batch proactively.
Some companies also use AI models to forecast product demand in specific city locations, enabling them to update inventory regularly.
There should never be a situation where a customer requests a product and it’s out of stock—this can lead to customer churn.
Latest Technology in Place
From finding the perfect location for dark stores to managing inventory, everything discussed above relies on having the latest, best-in-class technology.
A quick commerce business needs robust software at every step, and all systems should be seamlessly integrated.
Investing in cutting-edge technology and establishing training processes for staff will always benefit a business in the long run.
Wrapping Up
Quick commerce is now an industry with tough competition. Big brands are raising funds and rapidly expanding into small towns as well. However, to what extent quick commerce will flourish in small towns remains to be seen.
If you want to venture into it, the best approach is to choose a region and start something that caters to the local audience. List local products, source them from local vendors, and collaborate with local third-party logistics partners.
Starting locally requires less investment and, therefore, poses less risk. It also provides valuable insights into managing dark stores, inventory, and optimizing delivery routes.
