- GF/ SF - Tejas, Opp Hotel Prasadalay, Shukrawar Peth, Pune - 411002
- +91 90 2132 2132
Export Finance: A Complete Guide for Traders

Export finance is a tool that will assist you in dealing with the challenges of international trade. With global trade hitting over $33 trillion in recent years, the demand for financing solutions has skyrocketed.
Global markets are really exciting; however, there are many hurdles to cross. Problems such as payment security, currency fluctuations, and delayed payments are some of the risky factors discouraging many businesses from exporting. That’s where export finance steps in.
By using tools like trade credit, letters of credit, and export insurance, you can minimize those risks and ensure more seamless transactions. On the one hand, export finance creates wealth; on the other hand, economic ties between different countries are getting stronger.
What is Export Finance?
Export finance offers working capital to your business to cover the costs associated with international trade-involving shipping, manufacturing, and customs fees-in advance of payment from foreign buyers. It ensures smooth cash flow for exporters by bridging the gap between production costs and payment receipts. This delivers the opportunity to the exporters to meet orders and expand their business globally.
Export finance is primarily concerned with exporters (sellers), importers (buyers), banking institutions, and Export Credit Agencies (ECAs). ECAs provide trade finance, letters of credit, and insurance against trade risks such as slow payments and fluctuations in currency values. This type of financing is of immense help to small and medium-sized enterprises interested in expanding without financial constraints.
For Example: A company in the U.S. that sells machinery may deal with a buyer abroad. To minimize the risk of non-payment, the U.S. company may consider a letter of credit, a financial document issued by the buyer's bank that guarantees the payment to the seller only after fulfillment of certain conditions (for example, delivery of machinery). This gives assurance to the exporter and helps facilitate international trade.
Trade Finance vs. Export Finance: What Sets Them Apart?
Have a look at the image below to get a clearer idea of how Trade Finance and Export Finance differ.
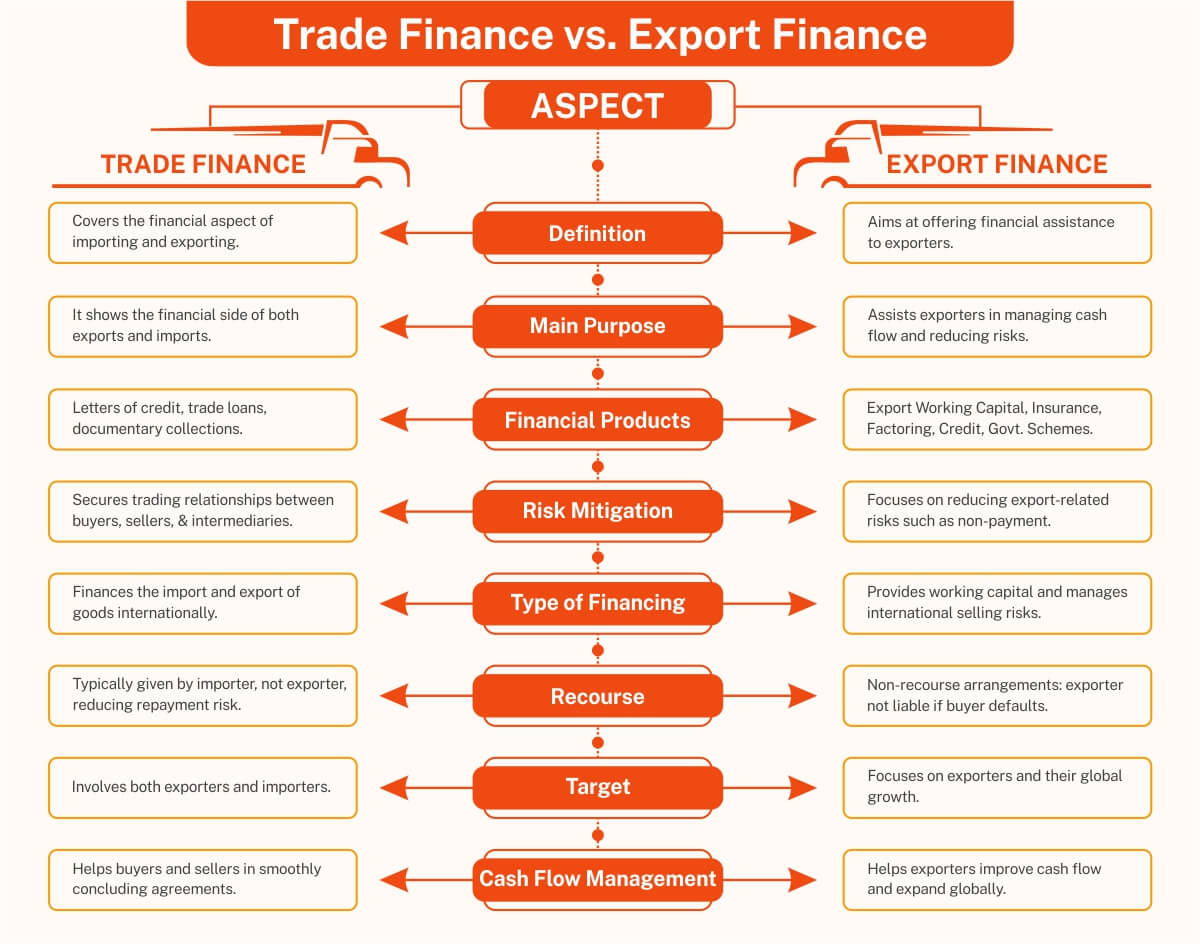
In short, export finance differs from trade finance in terms of trade flow. Export finance is working capital provided to a company to sell goods and services outside, while trade finance covers the financial needs of both imports and exports.
Now, let’s dive into - How Export Finance Works.
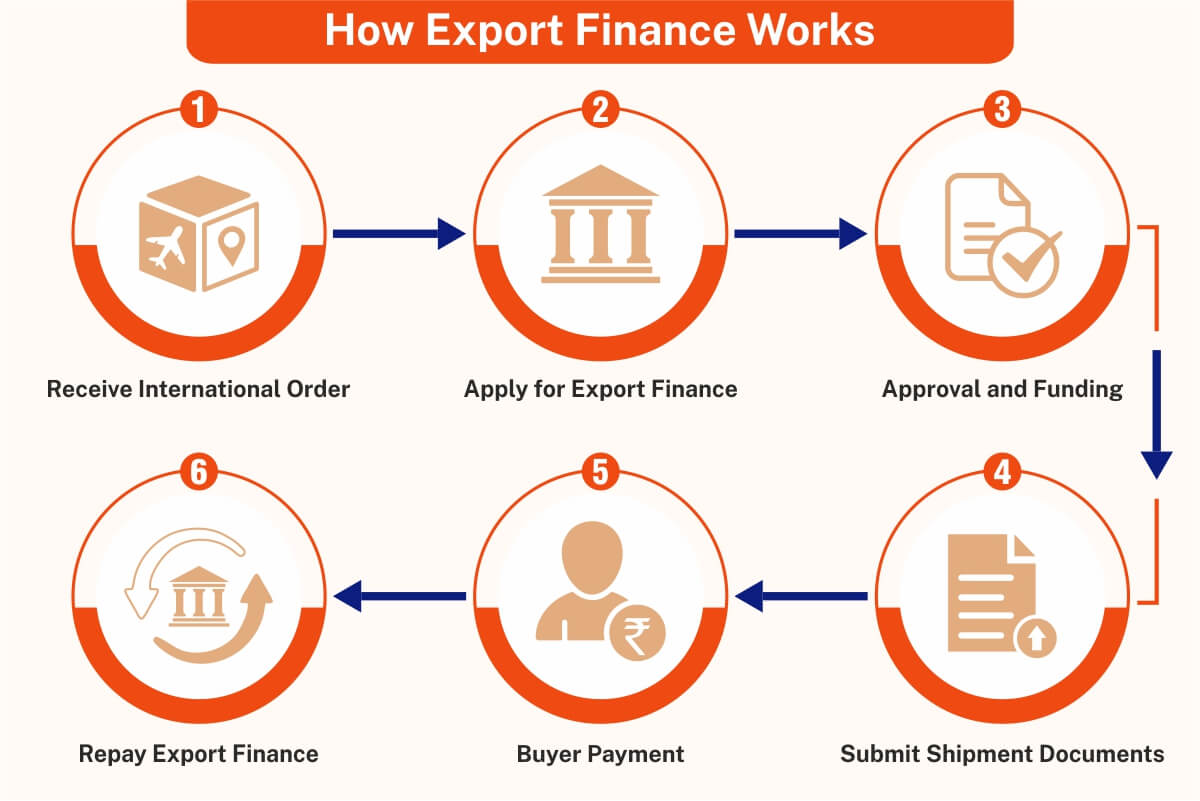
- Receive International Order: You receive an international order, but you need funds for production, raw materials, and packing.
- Apply for Export Finance: You apply through the bank, financial institution, or export credit agency for export finance with order and financial details.
- Approval and Funding: On approval of your application, the lender provides funds to commence production and shipping.
- Submit Shipment Documents: Submit relevant documents of international shipment to the lender.
- Buyer Payment: Upon receipt of the shipment by the buyer, they make payment as per the terms agreed upon.
- Repay Export Finance: You repay the export finance after receiving payment, and the remaining fund is your profit.
Let’s Discuss the Different Types of Export Finance
-
Pre-Shipment Finance
Exporters can access funds under pre-shipment finance before shipping a consignment. It normally covers production, manufacturing, packaging, and raw material costs. For example, Export Packing Credit covers physically producing and packaging, while Raw Material Financing covers the actual costs of raw materials consumed in production. This option ensures exporters can fulfill orders without waiting for buyer payment. It’s a key tool to manage costs and keep orders on track.
-
Post-Shipment Finance
When the goods have been dispatched, it requires additional costs. There will be a time gap between shipment and payment. In such a situation, invoice bills can be mortgaged with a bank. The importer will pay a certain amount upfront to the exporter and collect the remaining in due course. This ensures continuity of cash flow and meets financial obligations when awaiting payment, ensuring the smooth running of affairs.
-
Letter of Credit
A letter of credit guarantees that the bank makes payments once stipulated terms are met, thereby reducing the risk of nonpayment in international transactions. Here, the bank can also provide extra security against the payment being made under a loan, and that further eliminates risks. In short, this assures payment when conditions are fulfilled and transaction security.
-
Export business loans
Amazingly, this loan provides daily operation for export businesses such that it can produce and deliver without stressing its internal resources. Exporters can keep running and focus on their speed without much financial pressure.
-
Export credit insurance
International suppliers have to think a lot when it comes to the risk of nonpayment. Export credit insurance is there to compensate for any losses in case the buyer cannot proceed with the payment, either due to bankruptcy or financial problems. Such an assurance gives you peace of mind, knowing that your business is safeguarded against incoming payment risks.
-
Export Factoring
This financial service allows sellers to sell their invoices to a third party, known as a factor, at a discount. This way, exporters can maintain their immediate cash flow instead of having to wait for customers' payments. It is a good way to keep the business going and to quickly access funds tied up in receivables.
Looking for Export Finance? Here Are Some of the Best Options
-
Banks
Commercial banks serve as an important source of export finance. These private banks extend facilities for pre-shipment and post-shipment finance, provide trade credit, and deal in letters of credit. Such experience with international trade lends a lot of safety and flexibility to exporters while also providing excellent financial support.
-
Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) are government-owned financial institutions that assist in terms of export credit insurance coverage and guarantees and direct loans to exporters. They help with credit risks, such as nonpayment or market instability in international trade operations, making it safer for exporters.
-
Development Banks
Development banks, such as the African Development Bank and the World Bank, offer concessional loans and other forms of financial support for foreign trade. It focuses on developing markets and small businesses.
-
Trade Finance Providers
Trade finance organizations offer-services including flexible factoring, forfeiting, and working capital financing to support their client's cash flow. They offer quick and flexible alternatives, such as export letters of credit or invoice discounting, for traditional bank loans.
-
Government Programs
Governments make available grants, subsidies, and incentives for the promotion of exports, funding market research, international travel, and export infrastructure. They also finance exporters through specific programs with loan schemes and credit facilities.
Want Export Finance Without the Wait? Here’s How to Get It.
- Understand needs: Before approaching any application, determine the amount, purpose, and tenure for finance.
- Research options: Various types, such as post-shipment, pre-shipment, and trade credit insurance.
- Build a credit profile: A clean credit history maintained with clean records and little debt could help in increasing approval chances.
- Prepare documents: Collection of all relevant documents such as contracts, business plans, financial statements, shipping details, etc.
- Choose trusted institutions: To make transactions easy and smooth, work with credible financial institutions such as ECAs, commercial banks, and development banks.
- Submit application: Submit duly filled documents along with a proposal explaining the purpose and terms of financing.
- Use export credit insurance: This protects the firm against risks such as non-payment and political risk.
- Negotiate Terms: Compare financing offers and negotiate for lower interest rates and more favorable terms, including repayment schedule adjustments.
Export Finance Is Possible, But Here Are the Risks to Consider
- Late payments: Payments that take longer and affect cash flow and the conduct of business.
- Credit risk: Loss for exporters when importers fail to pay.
- Exchange rate risk: Payment may be reduced due to fluctuation in exchange rates, causing a loss.
- Political risk: Political incidents, including sanctions or wars, hinder exports and payments.
- Quality risk: When the product quality is gone, the customer can claim for rejection, refund, or discount.
- Fraud risk: Fake documentation or dishonesty of an investor can result in huge losses.
- Transport risk: Damage to, theft of, or delay of cargo while in transit adversely affects finance.
- Legal risk: This can generate fines or disputes within the navigation of many legal system fines or disputes.
Bottomline
Export finance opens doors to global trade by helping businesses manage risks and cash flow. Equip such a pre-finance with acquisition and export insurance for any delays caused by defaults or market fluctuations. Available trusted sources include banks and export credit agencies, among others, for cash raising. Go for the support you deserve, and you will walk with confidence in light of these open doors to new markets.
So, why wait? Explore your export finance options and let your business move with the velocity express of international growth.
