- GF/ SF - Tejas, Opp Hotel Prasadalay, Shukrawar Peth, Pune - 411002
- +91 90 2132 2132
Batch Costing : A Comprehensive Overview
Have you ever wondered how businesses keep track of costs when producing goods in bulk? Well, that needs batch costing. It is the method through which the company looks at the cost incurred by each produced batch.
In this post, we will discuss what batch costing is, its importance, and the relevant points that concern it. We'll also take a look at its comparison with job costing so that you may be able to decide which best approach meets your needs.
What is Batch Costing?
Batch costing generally refers to a costing method that is used to assign manufacturing costs to a particular batch or group of products, particularly in food, beverage, pharmaceutical, or chemical industries. This procedure involves calculating the total costs incurred for each batch, covering direct labor, materials, and factory overheads, and dividing this total cost by the number of items in a batch in order to arrive at the per-unit costing.
The system defines one batch as a unit of cost and allocates costs more simply. However, it can be very complicated, so an analyst must be experienced to ensure the accuracy and reliability of cost data.
Now that you know what batch costing is, let’s look at how to calculate it. Using a simple formula, businesses can determine the cost per unit within a batch, which helps in pricing and budgeting.
How to Easily Calculate Batch Costs?
Let’s say the total cost of producing a batch is ₹200,000, and the number of units produced is 20,000. Using the batch costing formula :
Batch Cost Per Unit = (Material Cost + Labor Cost + Overhead Cost) / Number of Units Produced in the Batch
Batch Cost Per Unit = ₹200,000 / 20,000 = ₹10 per unit
Now, if the size is 500 units, the total cost for that batch would be:
Total Cost for the units = ₹10 * 500 = ₹5,000
So, the cost of producing 500 units would be ₹5,000.
To better understand how batch costing works in real life, let’s explore some practical examples from different industries. This will give you a clearer picture of its execution.
See Batch Costing in Action with These Examples
Example 1: Production of Notebooks
A stationery company produces 1,500 notebooks in a single batch. To get the final cost of a notebook, the process involved in costing production is calculating the total production cost of that batch, which includes the materials, labor, and overhead costs, and dividing it by 1,500 units.
If the cost of producing one notebook is ₹50, then the total cost of producing the entire batch is:
1,500 notebooks × ₹50 = ₹75,000
Profitability per notebook is determined by the company so as to enable proper financial control through pricing or production quantity adjustments. Being the same, it becomes easier to identify the quality control problems to make necessary corrections quickly.
Example 2: Production of Motorcycles
Motorcycle manufacturing firms manufacture motorcycles in batches also known as production runs. The total production budget including materials, labor, and overhead costs is calculated for the entire lot, and then the costs are divided against the number of units produced to give the cost per motorcycle.
What would be the cost of each motorcycle when 500 motorcycles' production costs would be Rs.25 crore?
₹25 crore ÷ 500 = ₹5 lakh per motorcycle
It helps the manufacturer in calculating the profitability of each motorcycle sold and in making appropriate pricing, production quantity, and cost control decisions that would maximize profits.
Batch costing comes with several advantages that make it a valuable method for your business dealing with bulk production. Let’s explore how it helps in cost allocation, pricing, and efficiency.
Batch Costing Advantages: How It Can Help Your Business
-
Accurate Cost Allocation
Batch costing helps businesses calculate the exact cost of small batches or unique items, which ensures proper resource allocation and price accuracy in any context, especially for products that are not mass-produced.
-
Pricing & Cost Control
Batch costing helps in setting the right costs and managing expenditures to achieve adequate financial controls and establish the profit levels, batch costing remains essential in this context.
-
Cost Tracking at Each Stage
Batch costing enables the management of cost information from the different stages of production and shows where costs were incurred - whether they be raw materials, labor, or overhead - allowing the correct allocation of costs during production.
-
Overhead Cost Allocation
Costing by batch goes on to allocate costs, for example, utilities, rent, etc., into respective batches. This makes batch costs easier to compute since it determines the accurate cost per batch.
-
Improved Efficiency
Batch costing throws light in detail on cost insights allowing for recognizing inefficiencies, classifying operations, and eliminating waste, therefore increasing productivity, and in turn, leading to cost savings and profits.
-
Raw Material & Labor Tracking
Batch costing keeps a very close tab on raw material and labor broken down to a batch level to accurately calculate production cost which influences pricing decisions, check expenses, etc.
-
Production Efficiency Assessment
Batch costing helps businesses evaluate production efficiency by analyzing batch costs, identifying areas for improvement in material usage, labor, or production time, and implementing changes to optimize operations.
While batch costing has many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. In some cases, it may not be the best fit for a business. Let’s look at some of the hidden drawbacks.
The Hidden Drawbacks of Batch Costing
-
Rigidity
Batch costing is almost impractical for businesses that have a great many different kinds of products or services because batch costing for such types of manufacturing includes cost computations for each batch.
-
Low Efficiency
The allocation process of overhead costs to each batch could be fairly low on efficiency and could often lead to a misleading representation of the true cost of production.
-
Restricted Spending Control
Batch costing does not present detailed information on expenses for individual products or services. Which means it is unable to identify and control costs.
-
Quality Control Challenge
It becomes very hard at times to determine defective units costing. Batch costing does provide adequate visibility in identifying the defective units produced in a batch.
-
Difficult for Service Industries
Batch costing is more acceptable in the manufacturing industry to produce goods in batches. It becomes difficult to apply batch costing in the service industry since service must be provided to each customer individually.
Batch costing is often compared to job costing, another common cost accounting method. Understanding the key differences between these two can help your business choose the right approach.
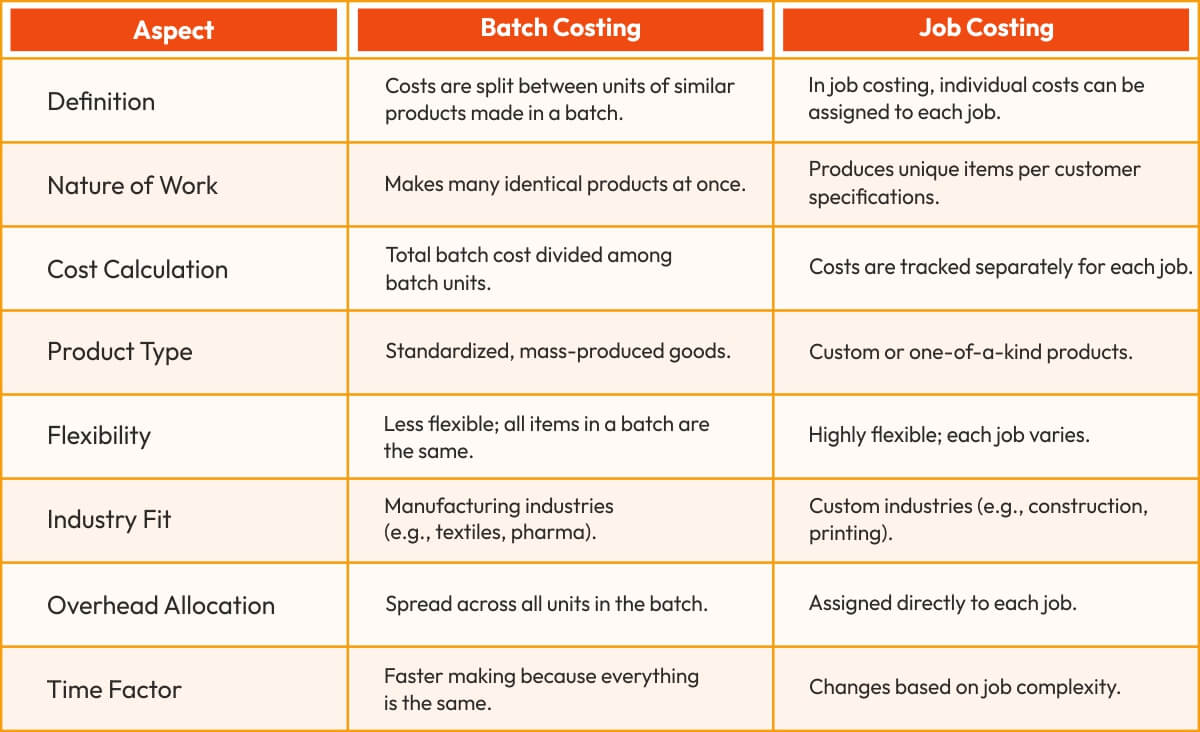
Batch Costing vs. Job Costing: Which One Fits Your Business?
Choosing the right costing method depends on your business needs. Here’s how batch costing and job costing differ.
Final Insights
Batch costing is a great way for your business to track costs when producing goods in bulk. This becomes very useful for accurate pricing, control of cost and enhances efficiency in general. This system is not perfect though because there are some industries which will need flexibility, or detailed tracing of cost, which probably a batch costing system cannot provide.
Knowing the difference between batch and job costing can help your business pick the best method for their needs. When used wisely, batch costing broadens operational efficiency, regulates costs, and maximizes profits.
